Download PDF For Details
1861 E Pole Road, Everson, WA
Phone 360-354-3912
Proper installation of the tank is absolutely critical for maintaining the water- tightness produced in the plant. Many of the problems experienced with leakage can be attributed to incorrect procedures during installation. In addition to damage to the tank, improper installation techniques could be a safety hazard.
Site Conditions The installation site must be accessible to large, heavy trucks weighing up to 80,000 pounds. The construction area should be free of trees, branches, overhead wires, or parts of buildings that could interfere with the delivery and installation of the septic tank. The truck must set up on level ground and have an area approximately 22 feet wide to be able to set down their outriggers. Most trucks will need to get within three (3) to eight (8) feet of the excavation to be unloaded.
The installation site must be accessible to large, heavy trucks weighing up to 80,000 pounds. The construction area should be free of trees, branches, overhead wires, or parts of buildings that could interfere with the delivery and installation of the septic tank. The truck must set up on level ground and have an area approximately 22 feet wide to be able to set down their outriggers. Most trucks will need to get within three (3) to eight (8) feet of the excavation to be unloaded.
Excavation
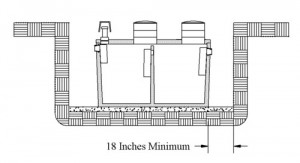
Prior to excavation, all buried utilities should be identified and located. Excavations should be made with approximately 18 inches of clearance around the installed tank to allow room for adequate compaction. More space should be provided, as needed, if work other than installation is required. Excavations should be sloped to comply with all construction safety requirements.
Bedding
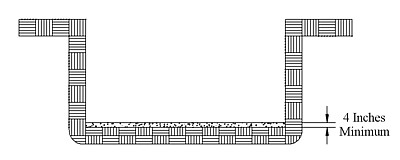
Proper use of bedding material is important to ensure a long service life of an onsite septic system. Bedding material should be used as necessary to provide a uniform bearing surface. A good base should ensure that the tank would not be subjected to adverse settlement. A minimum 4 inches thick sand or granular bed overlying a firm anduniform base is recommended unless otherwise specified. Tanks should not bear on large boulders or massive rock edges. Sites with silty soils, high water tables or other “poor” bearing characteristics must have specially designed bedding and bearing surfaces.
Correct compaction of the underlying soil and bed is critical
to ensure there is no differential settlement.
Tank Placement
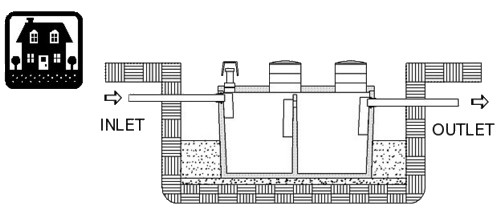
Prior to placement in the excavation, the tank’s orientation should be confirmed. Inlet penetrations should face the residence and the bedding material should be checked. After placement, check that the tank is level. The slope of the sewer line and tank should meet local plumbing and building codes.
Joint Seals
For two-piece tanks use high quality preformed joint seals. Surfaces should be clean. Seals shall meet minimum compression and other installation requirements as prescribed by the seal manufacturer and detailed herein. Tank sections sealed on site should not be backfilled until the sealant has settled. Manholes must be properly sealed as well.
Backfilling
Backfill should be placed in uniform, mechanically compacted layers less than 24 inches thick. This fill should be nearly equally placed around the tank. Backfill should be free of any large stones (>3 inches diameter) or other debris. Each layer should be adequately compacted. If the water level in the hole is allowed to rise to a high level, concrete tanks can float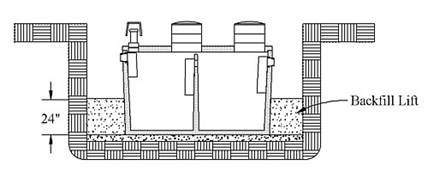 . To prevent floatation during backfilling, fill the tank with water, place soil on top of the tank or keep water pumped out of the hole until backfilling is completed.In extremely cold weather, it might be necessary for tanks to be insulated before backfilling. Cold temperatures tend to impede a tank’s natural ability to digest wastes through anaerobic processes. Once the anaerobic process begins, cold should have no impact unless the tank is not utilized for long periods.
. To prevent floatation during backfilling, fill the tank with water, place soil on top of the tank or keep water pumped out of the hole until backfilling is completed.In extremely cold weather, it might be necessary for tanks to be insulated before backfilling. Cold temperatures tend to impede a tank’s natural ability to digest wastes through anaerobic processes. Once the anaerobic process begins, cold should have no impact unless the tank is not utilized for long periods.
